
Lately, Bitcoin has undoubtedly created a lot of buzz. Warmly received by tech enthusiasts and the unbanked people of developing nations, it is often claimed that bitcoins can be transferred free of cost — this helps up as one of the ways it brings about ‘financial freedom’. This, however, isn’t entirely correct. In most transactions, you do end up paying a nominal fee as charges.

What Is The Fee For?
Every day, thousands of transactions are sent and received on Bitcoin’s network. These transactions need to be ordered and documented on the global ledger that records every Bitcoin transaction ever made. The fees are given to miners who provide the record-keeping service for Bitcoins. In our ultimate guide to bitcoin, we’ve discussed the incentives miners need to stay connected to the network. Mining is extremely critical to keeping the network secure. A large network hash (or mining) rate keeps Bitcoin safe from attacks by bad actors. This fee is given to them as an incentive to keep mining, which in turn keeps the bitcoin network secure.
Like our banking fee, this fee also has a set of well-defined rules and regulations that are established as “network rules”, and a fee is levied on each transaction accordingly.
Once a majority of the Bitcoins are mined, the transaction fee becomes the primary earning of the miners. Fees incentivize miners to include transactions in a block. Once a transaction has been included in a block it is confirmed.
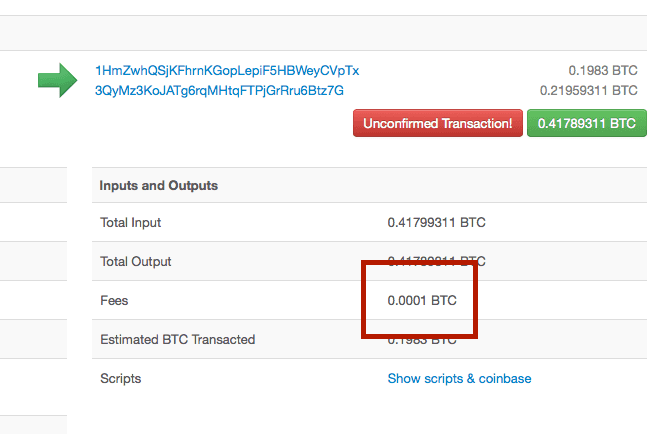
How Is Transaction Fee Calculated?
An array of parameters are considered for determining the value of transaction fees, which we’ll list out here:
- Dust Spam: If the value of any transaction amounts to less than 0.01 BTC, then a fee of 0.0001 BTC is required. Therefore, the algorithm for coin selecting tries to avoid using an amount less than 0.01 XBT whenever possible.
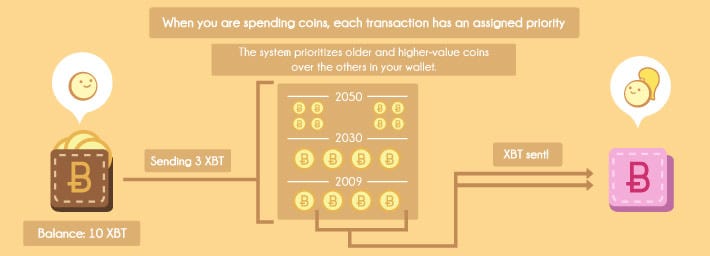
- Prioritise old & high- value coins: If the coins used in a transaction are new, or amount to a small value, they are given low priority. The priority is assigned on the basis of age, size, and number of inputs.
- The difference in Input & Output Amount: The transaction fee could be the difference in the input amount (sending funds) and the output amount (receiving funds) of the transaction. For example, if the input equals 0.12605724 and the output equals 0.12583356. The fee, 0.00022368, is actually the difference between these two numbers.
While the process of calculating these transaction fees seems complex, you — the end user — don’t have to worry since all this is taken care of by the bitcoin software clients or online exchange services like Unocoin.
Why should you invest or trade in bitcoin in the first place, you ask? This post on the phenomenal rise of Bitcoin should help you.
To summarise
- Mining is used to record the transactions and maintain a global ledger for bitcoins — this is funded by fees for the miners.
- Transaction fees are determined based on parameters like age, size, and amount of coins.
- Bitcoin wallets such as Unocoin get rid of all this complexity by charging a flat fee for transactions so you can invest and trade in peace!




