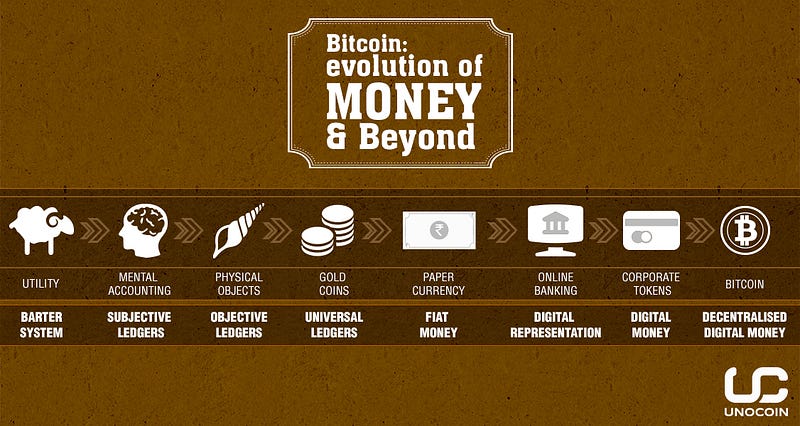
Concept of Money
Barter system was provably inefficient in terms of portability, divisibility and mainly accountability. Money has its roots as an abstract form of accounting (Subjective Ledger Technology) used to facilitate a closed community trade goods and services inside their system.
Growing population and impractical methods to maintain subjective ledgers beyond a community lead to objective ledgers underpinning value to physical objects such as sea shells.
With time, we have seen emergence of standardised attributions of money especially to rare metals (universal ledgers) which comply physical limitations around the globe and made it easy for accountability, portability and divisibility.
However, with massive industrialisation driving humongous amounts of trade and commerce worldwide gave birth to a more powerful technology of fiat currency which is more portable, divisible and fungible aiding the problem of accounting. Further, 21st Century has seen the dawn of digital money as an abstract representation of physical fiat currency for online transactions.
Problems of Money (Need for Bitcoin)
Decoupled abstraction of fiat currency with the introduction of cash reserve ratios brought new financial troubles of fraud (counterfeiting, digital hacking) and unpredictability to the economy giving rise to inflationary economics.
Apart from these, some notable flaws in the current underlying economic frameworks are:
- Delayed transaction settlements
- Totalitarian accounting and Unpredictable money supply
- Higher cost per transaction
- Transaction reversibility and the origin of fraud
- Double spending and digital security vulnerabilities
- Fragmented currency networks
Bitcoin has been the definitive answer to these problems by building an alternate currency system which is more evolved and robust adopting a decentralised model with no central vulnerabilities to trust upon.
Solution Behind (Blockchain Technology)
While Bitcoin is the end solution, blockchain technology powering Bitcoin is the fascinating invention that made it possible with a combination of technical tools such as
- P2P networking – for an efficient and open system
- Proof-of-Work algorithm – to make the system more robust and secure with open competition
- Cryptographical ownership – financial inclusion and impractical to break privacy
- Transaction based ledger (UTXOs) – introducing immutability and solving double spending problem
- Scripting capability – helping nodes to validate pseudonymous transactions and build complex transactions
- Merkle Root mechanism – utilise the power of blockchain without hosting a full node (complete blockchain)
Beyond Money (Evolution of DApps Frameworks)
Blockchain has caught a serious attention lately by industry leaders impressed with the power to facilitate autonomous trade and smart contracts between two unknown parties without trust.
Continuous iteration and development of blockchain is very evident with four major evolutionary steps it took:
Iteration One (On Bitcoin blockchain)
Borrowing the advantages of immutability and data redundancy backed with network security, we have seen adoption of Bitcoin blockchain for storing critical data points of an application/ use case such as tracking real world assets.
Iteration Two (Forking Bitcoin blockchain)
While Bitcoin blockchain offers limited scope for building only complex financial transactions, a different iteration/fork of this blockchain has shown the possibility of building a completely turing complete scripting possibility on top of blockchain making it possible to write completely open decentralised server code for the first time.
Iteration Three (Codebase to bootstrap blockchains)
There have been multiple instances and specific requirements from enterprise communities for a more specialised advantage of blockchain with added privacy and accessibility management leading to a multiple open source code repositories which can help you kickstart your own public/private blockchains suitable for your applications.
Iteration Four (Blockchain as a Service model)
More rapid adoption and emergence of blockchain as a critical technology for open and secure systems for applications shared between multiple parties arises a definite learning curve for adoption. We are already seeing popular cloud services already embracing this technology stack labelled as ‘BaaS’ (Blockchain as a Service) offering a plug and play model for developing more personalised blockchains.
While Bitcoin is the first practically famous application of blockchain technology, we are yet to unleash a world with the core communication and accounting infrastructure built on blockchain.



