
As more and more firms incorporate the blockchain technology into their corporations, are traditional databases losing their significance? To apprehend how blockchain technology and databases work, it is important to consider their differences by understanding their design and functions.
Structural difference
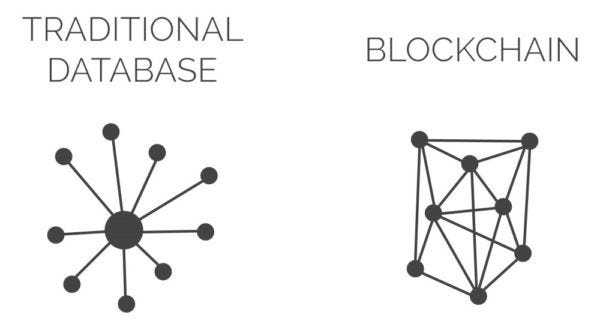
A database basically uses a client-server network structurally. A database administrator is the one that can make changes to any part of the data or its structure at any given point in time. These database administrators are the central authorities who are responsible for maintaining the control of the database. They are also in charge of deciding who can get the permission to access its information.
On the other hand, a blockchain in itself is a database — but in the form of a digital ledger. It puts together internet along with cryptography and eradicates the need for a trusted middleman (e.g.: a bank — in case of monetary transactions). In a blockchain, information is put together in an array of ‘blocks’ of data. Each of these blocks is connected to its preceding one through a hashing function. This, in turn, forms a chain of blocks that cannot be changed, hence making the data immutable and secure.
In a database, stored data can be modified, changed or even deleted without any trouble. However, in the case of the blockchain, it is close to impossible to modify, change or delete data. In fact, unalterable data is a key feature of the blockchain technology.
Decentralization aspects
A distributed database is appropriate for organizations and companies wherein every user trusts the other user and does not intend to keep any duplicate record of the same data.
However, when it comes to the blockchain technology, transactions that take place are verified by consensus from other nodes that are present on the same blockchain. This tends to make the process more reliable and protected. It is trust-less, as in, it doesn’t require trust in the first place.
Functional aspects
By the means of a traditional database, a client is able to perform four different functions on data, that is — Create, Read, Update, and Delete (these are collectively called as the CRUD commands).
The blockchain, on the other hand, is designed differently when it comes to functioning amidst data. A user can only add more data to the already existing one in the form of additional blocks. All of its previous data is permanently stored and hence is impossible to alter with. Therefore, the only associated operations include:
Read Operations: Retrieving existing data from the blockchain.
Write Operations: Addition of more data onto the blockchain.
An intermediary tends to maintain the privacy of records in a database. However, the blockchain technology makes all records of sorts completely public. This kills the need for a middleman, especially since the information is accessible to all. Moreover, anyone attempting to cheat this system can easily be identified.
In competitive markets, many businesses tend to incline towards the privacy of a centralized database, rather than publicly display their activities.
Cost and expenditure
Blockchain technology has helped in removing much complexity of setting up a self-distributed database. This, in-turn, cuts down costs significantly, considering the reductions in prices due to collective payments.
Blockchain vs Databases
While both have advantages and disadvantages of their own, the right choice out of the two would completely depend on the business’s or the company’s preferences. That is, whether they’re looking for transparency and reliability or privacy and control — it is entirely dependent on their proclivities and priorities.
Also Read:
https://blog.unocoin.com/a-world-where-cryptoassets-are-securities-a032bb156e18



![Fundamental Analysis in Crypto [Updated Guide] A Comprehensive Guide to Asset Valuation.png](https://blog.unocoin.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/A-Comprehensive-Guide-to-Asset-Valuation-218x150.png)